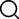
Tempered glass production equipment forms surface compressive stress and internal tensile stress through physical tempering (heating to the softening point and then rapid cooling). The core equipment includes heating furnaces, cooling devices, and automated control systems. It can produce flat tempered, curved tempered, and shaped tempered glass, featuring enhanced strength, improved safety, and temperature resistance. The following is a detailed explanation of key equipment and its functions:
1. Core equipment composition
heating furnace
Function: Heat the glass to 600-650℃ (close to the softening point) to ensure even heating.
Technical features:
The use of radiant heating or forced convection technology, such as upper forced pure convection technology, ensures uniform heating of the glass and reduces thermal stress.
Equipped with imported silicon ceramic roller tables, it has strong bending resistance, large effective load capacity, and reduces heating defects.
The furnace body is made of high-density insulation board to reduce heat loss, ensuring a temperature drop of only 150℃ after 12 hours of insulation during a power outage.
Cooling device (air grille section)
Function: Rapidly cool the heated glass through high-speed airflow to form a surface compressive stress layer.
Technical Features:
The air grating section consists of upper and lower air blades made of stainless steel, with their heights individually adjustable.
The airflow system is compatible with both flat and curved glass tempering, featuring automatic air pressure adjustment and electric balance of air volume.
Equipped with an emergency film ejection function, it allows for manual or electric film ejection in case of a power outage, thus preventing glass damage.
Automated control system
Function: To achieve precise control over parameters such as temperature, wind pressure, and transmission.
Technical Features:
The system integrates Siemens PLC and industrial computer, supporting online modification and storage of process parameters.
Equipped with a touchscreen human-machine interface, it offers intuitive operation and supports fault diagnosis and remote maintenance.
Equipped with data recording and analysis functions, it optimizes production processes.
II. Key Process Flows
Upper piece and positioning
The glass is conveyed to the front of the heating furnace via a roller conveyor, where a photoelectric switch and a rotary encoder measure the glass size and automatically adjust the step length.
The auxiliary lifting mechanism simplifies the placement of large glass sheets, enhancing operational safety.
Heating and homogenization
The glass moves back and forth within the heating furnace to ensure uniform temperature and prevent thermal stress concentration.
The temperature homogenization section further eliminates temperature differences, laying the groundwork for subsequent cooling.
Quenching and tempering
The heated glass is quickly moved to the air grating section, where high-speed airflow is symmetrically sprayed, causing rapid cooling on the surface and forming compressive stress.
Internal cooling lags, resulting in tensile stress, and the overall stress balance enhances the strength of the glass.
Lower piece and inspection
The tempered glass is conveyed to the unloading table via a roller conveyor, and then manually or by a robotic arm for glass piece retrieval.
Equip inspection lights for the outgoing segments to detect the quality of the glass surface and ensure the absence of defects such as wind spots and stress spots.
III. Equipment types and applicable scenarios
Horizontal roller hearth tempering furnace
Application scenarios: Production of flat tempered glass for building curtain walls, furniture glass, home appliance glass, etc.
Technical features:
Supports continuous or reciprocating swing production, adapting to glass of different specifications.
It can be expanded with ultra-thin glass tempering function, processing 1.8mm thick tempered glass.
Bent steel furnace
Application scenarios: Production of curved tempered glass, such as car windshields and curved skylights.
Technical Features:
Equipped with a molding and quenching device, program-controlled camber curvature, achieving precise bending.
Supports the processing of irregularly shaped curved glass, such as J-shaped, S-shaped, and U-shaped, with a maximum size of 3000mm×2000mm.
Unequal arc tempering furnace
Applicable scenarios: complex curved glass, such as art decorative glass and irregular architectural glass.
Technical features:
The adoption of compound transmission synchronization technology reduces damage to the glass surface.
The multi-action combination structure enables flexible processing and is compatible with various glass types with gradual curvature changes.